Common menu bar links
Breadcrumb Trail
ARCHIVED - Treasury Board of Canada Secretariat - Modern Management Practices Assessment -- Findings
 This page has been archived.
This page has been archived.
Archived Content
Information identified as archived on the Web is for reference, research or recordkeeping purposes. It has not been altered or updated after the date of archiving. Web pages that are archived on the Web are not subject to the Government of Canada Web Standards. As per the Communications Policy of the Government of Canada, you can request alternate formats on the "Contact Us" page.
Background
Introduction
The government is undergoing rapid and significant change in the ways in which it both goes about its business, and chooses to manage itself. It is changing its culture and the way it manages resources. Modernized comptrollership is key to that transformation. This has involved a shift in emphasis from controls and compliance to results and values. Central to this theme is a shift of primarily financial focus to a broader management perspective.
In 1997, an independent review panel was created to facilitate renewal and change of the comptrollership function in government for the future. Based on the criteria identified in the panel's report, a self directed assessment tool was developed by KPMG Consulting L.P. to allow departments to assess their current practices against the recommendations and findings of the panel.
Modern comptrollership means sound management practices. Traditionally, comptrollership in government has focused on financial controls and accounting functions such as processing transactions, reporting totals and keeping track of funds. It has been regarded largely as the preserve of functional specialists. Modern comptrollership changes the emphasis from controls and compliance to results and values. It represents a shift from a centralized financial focus to a broader management perspective and thus becomes an integral part of each manager's responsibilities. It is about vigorous management of public resources with emphasis placed on performance and not just on following the rules. It is also about linking financial information (budgets, expenditures, revenues, assets, etc..) with non-financial information (planned results, performance, outputs, etc..). It focuses on effective decision making with sound management of resources, ranging from human, financial, capital and technological.
The Treasury Board Secretariat is one of twelve pilot departments leading the implementation strategy of Modern Comptrollership. Each of the twelve pilot departments undertook a self assessment of their practices in relation to the recommendations in the panel report using the Capacity Check Tool. This report reflects the results of interviewing forty managers within TBS.
Some key characteristics
- The KPMG Capacity Tool is a self assessment tool. For the purposes of the pilot departments, it was a "directed self assessment" in that a team of three consultants carried out interviews with managers. An interview guide was used to obtain manager's perceptions on each of the six elements.
- The interviewees were selected on the basis of balanced coverage for the Secretariat. This included managers at various levels in each of the branches/sectors along with some functional specialists.
- The review looked at process only and not the quality or product of the process.
- The Capacity Check Tool provides a rating system of "1" through "5". A higher rating does not necessarily mean "goodness", but rather, formality or maturity of capability. The ideal rating for any area is dependent on the needs and goals of the organization. The results of the review should be construed as a "baseline" against the criteria and not a "report card".
- The findings have been worded as neutrally as possible. Since the capacity check was not an audit we did not assess whether a finding was "good" or "bad". For example, a finding such as "There is no formal ethics framework" is neither a criticism nor a compliment but merely a finding.
- Interviewees were assured confidentiality in the interviews.
- The findings are at the Secretariat level and not at the branch or sector level. No branch/sector to branch/sector comparisons were carried out.
Executive Summary
Summary of Management Capacity Self Assessment
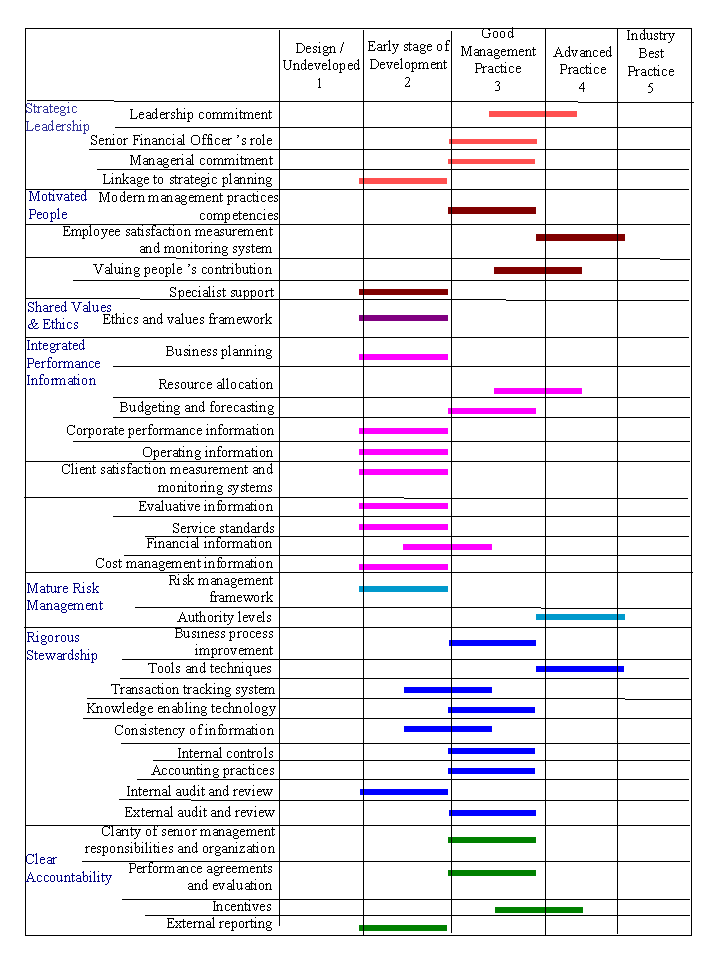
Below is a summary of the findings for each of the elements. The findings are described in detail in the Results section later in the report.
Key messages
- TBS has, for the most part, management practices in line with the modernization of comptrollership initiative for government.
- The commitment by senior management is strong, and there are many initiatives underway. Future focus should be to ensure that the culture permeates the organization.
- The level of service in functional support could be enhanced and many managers associated this with the impacts on resources in these areas through Program Review. Specialist support is seen as more process based and less so as a strategic business partner by managers throughout the Secretariat.
- Progress has been made in business planning and the process continues to mature.
- No formal risk management framework is in place.
- There is only limited definition of competencies required of managers in modern management practices.
- Management training is available but workload inhibits access.
- Ethics have not been clearly articulated and can therefore not be monitored on an ongoing basis.
- Limited capability to reallocate resources across branches or sectors.
- Evaluation frameworks have not yet been developed in some program areas.
- Limited formal costing systems in place but managers indicated that cost information is adequate for their needs.
- Managers are proud to work at TBS and there are strong values stated but managers also indicated actions or results do not always reflect intentions.
Overview
Objectives of the modern management practices capacity check
- Assess state of comptrollership practices within each department against a common standard. Assess current management practices against recognized best practices and principles as outlined in the Report of the Independent Review Panel.
- Bring together all the elements of the management framework. The capacity check is intended to integrate the full range of capabilities necessary to implement modern comptrollership, including leadership, business planning, risk management, performance management, control systems, and accountability management.
- Compare against best practices. The capacity check is based on best practices of other leading organizations, and therefore provides an opportunity for organizations to assess where they stand relative to these best practices.
- Provide assurance to external clients/stakeholders of the soundness of comptrollership within the Secretariat. The capacity check should help to clarify for external clients and stakeholders (e.g..., central agencies, Parliamentarians) the management approach that is currently in place, and to provide some assurance that the overall management framework is in sound order.
Key characteristics
- Future oriented--focuses on what capabilities must be in place in the future to respond to emerging client demands/changing environment.
- Focuses on expanding/improving capability rather than downsizing.
- Recognizes that an organization can only focus on selected improvement areas at any one time, and cannot be "best" at everything.
- Intended as a diagnostic tool for senior management of the organization.
- Departmental focus--not intended to compare management practices between sectors/regions.
- Directed self-assessment tool--not a review or audit. Information is collected through interviews, and then validated by the managers collectively.
- Builds upon changes already underway to existing management processes.
Key modern management practices elements examined
Modern Management Practices
- Strategic Leadership
- Motivated People
- Shared Values and Ethics
- Integrated Performance Information
- Mature Risk Management
- Rigorous Stewardship
- Clear Accountability
Strategic Leadership
Shared Values & Ethics
|
Integrated Performance Information
Mature Risk Management
|
Rigorous Stewardship
Clear Accountability
|
Project objectives, scope and methodology
Objective
- The objective of this project was to carry out a comprehensive assessment of management practices in the Treasury Board Secretariat in relation to the recommendations made in the Report of the Independent Review Panel on Modernization of Comptrollership in the Government of Canada. The team was to gather and analyze data to allow management to identify existing strengths and weaknesses in this regard.
- The assessment was to build upon existing processes and practices and assist in the identification of those areas where capability improvements are required in the Secretariat.
- The KPMG project team was to work with TBS staff to ensure a knowledge transfer of both the use of the Capacity Check tool and process required so that the Secretariat would be in a position to carry out future assessments using the KPMG Capacity Check tool.
Scope
- The assessment covered all organizational units in TBS and involved different levels of managers and functional staff.
The mechanics of the capacity check checklist - How it Works
- Current capabilities are assessed based on key elements of Comptrollership and criteria provided for each key element.
- The capabilities depicted within each criteria represent different states or plateaus that the organization may strive to achieve. The descriptions are incremental.
- The capability descriptions are based on generally recognized best practices, but have been customized to reflect the Independent Review Panel report and TBS assessment framework.
- A rating system of "1" to "5" is used. A high rating does not necessarily mean "goodness", but rather, formality or maturity of capability. The ideal rating for any area is dependent on the needs and goals of the organization.
TOPIC: Corporate Performance Information (TBS meets the criteria for level 2
|
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
| No corporate performance measures | Each Sector measures performance at corporate level. Organization-wide priority areas to be measured have been identified. | High level strategic measures are in place, and are linked to key strategic vision and priorities. Results to be measured under corporate measures have been identified, and are linked to measures throughout organization. | Performance results exist for the organization as a whole. Results are interpreted using a balanced scorecard philosophy. Results are monitored over time. Corporate measures are refined on an ongoing basis. | Results of corporate measures are monitored over time. Strategic and business plans are modified accordingly. Results of corporate measures are used to make trade offs in priorities. Information is readily accessible through executive information systems. |
|
Existing capability |
Future capability | |
| Where the organization may strive to be in the future |
Approach taken in TBS
The following steps were carried out in this review:
- A briefing was made by Secretariat staff to the KPMG consultants on the business and organizational structure of the Secretariat. Key documents to assist the team were identified and provided.
- The consultants and Secretariat team members identified the appropriate managers and functional staff to participate in the interviews. The protocol and process for carrying out the interviews was established. This included a communications strategy in order to prepare the interviewees.
- An interview guide was developed and tailored to suit Secretariat requirements.
- Interviews were carried out with 39 managers. Approximately half-way through the interview process, an interim analysis was carried out to ensure coverage and identify gaps in the information required. Adjustments to the interview process were made accordingly. TBS team members sat as observers on many of the interviews during the process.
- A project team workshop was conducted to consolidate all of the information received from these interviews and documentation. An analysis against the criteria in the diagnostic tool was made arriving at a tentative Secretariat rating for each element of each function. TBS team members participated in this workshop as an integral part of the knowledge transfer component.
- Three separate focus groups of approximately six to ten managers or functional specialists in each were carried out. The first focus group consisted of members of the TBS working group, the second was drawn from those participating in the original interviews and the third was made up of managers that had not previously participated in the process. The purpose was to validate the assessment ratings and to obtain a better appreciation of the level of consensus regarding the ratings. Several changes were made to the findings and ratings as a result of these validation sessions.
- A draft report was prepared, reviewed by Secretariat team members and the report amended accordingly.