Common menu bar links
Breadcrumb Trail
ARCHIVED - Canadian Space Agency
 This page has been archived.
This page has been archived.
Archived Content
Information identified as archived on the Web is for reference, research or recordkeeping purposes. It has not been altered or updated after the date of archiving. Web pages that are archived on the Web are not subject to the Government of Canada Web Standards. As per the Communications Policy of the Government of Canada, you can request alternate formats on the "Contact Us" page.
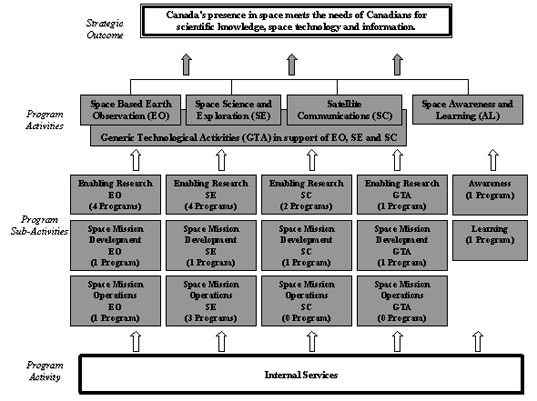
Section 2: Analysis of Program Activities by Strategic Outcome
The following detailed analysis outlines how program activities contribute in various degrees to the attainment of the strategic outcome, how key programs and services contribute to program activity priorities, and how the CSA will report on its performance over the coming years.
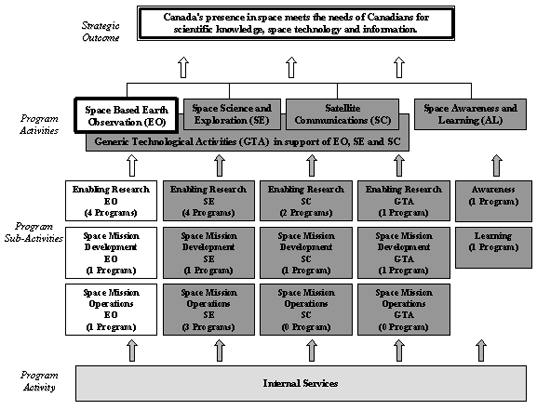
2.1 Space Based Earth Observation
Program Activity Priority: Develop and operationalize the use of Space Based Earth Observation (EO) for the benefit of Canadians.
|
Space Based Earth Observation (EO) Program Activity Performance Measurement |
|
| Expected Result #1 | Performance Indicators |
|
The benefits of activities of Earth Observation from space serve Canadians users in the areas of the environment, resource and land use management, and, security and sovereignty. |
|
|
Planning and Reporting Continuity: RPP 2007-2008: |
|
|---|---|
|
Resources |
2008-2009 |
2009-2010 |
2010-2011 |
|
Financial ($ in millions) |
129.2 |
126.1 |
128.4 |
|
Human (FTEs) |
82.2 |
81.6 |
67.1 |
The programs under this Program Activity are divided into three Sub-Activities: Enabling Research, Space Mission Development and Space Mission Operations.
Enabling Research – Earth Observation
Objective: Provide leadership, coordination or support to Earth Observation (EO) applied research and experimental development in line with the CSA priorities and stakeholders expectations in order to increase the knowledge base and devise new applications through space missions, and to allow the transfer of intellectual property and proven technologies to Canadian industry, academia, and government organizations.
| Expected Result #1 | Performance Indicators |
| New project/mission concepts that progress to subsequent development phases related to Agency priorities. |
|
| Expected Result #2 | Performance Indicators |
|---|---|
| The CSA's in-house personnel are highly qualified, with recognized expertise, and are supported by a high-technology infrastructure that is suited to all enabling research projects/missions. |
|
|
Resources |
2008-2009 |
2009-2010 |
2010-2011 |
|
Financial ($ in millions) |
26.8 |
28.0 |
24.1 |
|
Human (FTEs) |
16.6 |
13.0 |
12.8 |
Main Expected Accomplishments:
- Following the successful launch of RADARSAT-2 in December 2007, the Canadian government data allocation plan will be implemented to manage the $445 million worth of prepaid data from the satellite. The objective of the program is to ensure that the Canadian Government effectively uses the allocation.
- Through the Earth Observation Application Development (EOADP) and the Government Related Initiatives (GRIP) Programs, the CSA will continue satellite data application development and utilization, to support the growth of EO capabilities within Canadian Government Departments and within value-added industry.
- The CSA will complete the assessment of the requirements of the Canadian government users for a polar satellite system as part of a joint study with Department of National Defense and Environment Canada. The Concept of the Polar Communications and Weather Mission is to put a constellation of satellites in highly elliptical orbit over the North Pole to provide communication services and monitor weather in the Arctic region.
Space Mission Development – Earth Observation
Objective: Provide coordination or support to the development of Earth Observation (EO) space missions in line with CSA priorities and stakeholders expectations through the definition, critical design, manufacturing, integration, testing and delivery phases leading to launch and early operations of space systems.
| Expected Result #1 | Performance Indicator |
| Space mission proposals that efficiently, effectively and economically progress to subsequent operations phases in accordance with objectives, requirements, initial or revised specifications. |
|
| Expected Result #2 | Performance Indicators |
|---|---|
| The CSA's in-house personnel are highly qualified, with recognized expertise, and are supported by a high-technology infrastructure that is suited to all Space mission development projects. |
|
|
Resources |
2008-2009 |
2009-2010 |
2010-2011 |
|
Financial ($ in millions) |
86.7 |
89.0 |
94.7 |
|
Human (FTEs) |
34.0 |
40.7 |
20.8 |
Main Expected Accomplishments:
- With the successful launch of RADARSAT-2 on December 14, 2007, its commissioning and transition to routine operations will be completed by April 2008. The CSA will close the RADARSAT-2 Major Crown Project by September 2008.
- Further progress will be made in the development of the next generation of RADARSAT satellites, and risk mitigation activities will be carried out on the SWIFT instrument.
Space Mission Operations – Earth Observation
Objective: Provide coordination or support to the operations of Earth Observation (EO) space missions in line with the CSA priorities and stakeholders' expectations through the development and conduct of on-orbit operations, system maintenance and logistic support, as well as data handling and delivery.
| Expected Result #1 | Performance Indicator |
| Space mission operations are managed effectively and efficiently. |
|
| Expected Result #2 | Performance Indicators |
|---|---|
| The CSA's in-house personnel are highly qualified, with recognized expertise, and are supported by a high-technology infrastructure that is suited to all Space mission operations. |
|
|
Resources |
2008-2009 |
2009-2010 |
2010-2011 |
|
Financial ($ in millions) |
15.6 |
9.1 |
9.6 |
|
Human (FTEs) |
31.6 |
27.9 |
33.5 |
Main Expected Accomplishments:
- RADARSAT-1 operations will continue with the usual level of high performance for satellite reliability and image production, and the supply of data to Canadian Government clients from RADARSAT-2 will begin in 2008 upon the commissioning of RADARSAT 2 as per client needs. With two satellites in operations data continuity to users is more assured. Moreover, a contingency plan is
in place to secure the use of foreign sensors as backup in order to continue to meet the needs of operational users if Canadian satellites were unable to meet this requirement. This contingency plan provides and equivalent back-up capability using RADARSAT-1 and -2 data to ESA in case of national asset failures.
- The CSA will continue to operate SCISAT, a Canadian mission launched in 2003 that is providing a large amount of very high quality data on more than 30 chemical species in the atmosphere for climate, weather and pollution studies. Through an agreement with ESA and NASA, the data from those SCISAT orbits not accessible from Canada will be received by ESA and NASA receiving stations and provided to Canadian scientists, which greatly expands the range of coverage.
To learn more about the Earth Observation Program Activity, go to: www.space.gc.ca/asc/eng/resources/publications/default.asp#parliament
To learn more about Earth Observation, go to: www.space.gc.ca/asc/eng/satellites/default.asp?page=observation
2.2 Space Science and Exploration
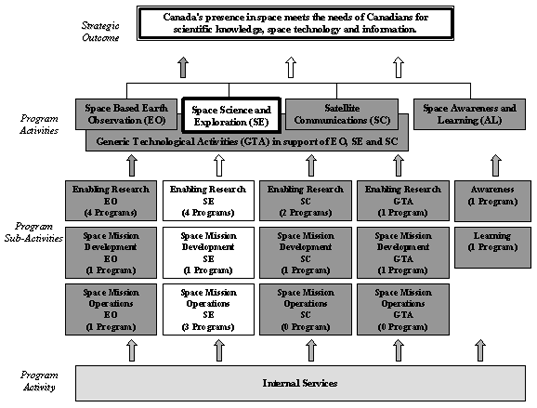
Program Activity Priority:Understand the Solar System and the Universe, expand our knowledge on the constituent elements and origins of life, and strengthen a human presence in space.
|
Space Science and Exploration (SE) Program Activity Performance Measurement |
|
|---|---|
| Expected Result #1 | Performance Indicators |
|
Participation in Canadian and international missions expands the scientific knowledge base made available to Canadian academia and R&D communities in the areas of astronomy, space exploration and solar-terrestrial relations, as well as in the physical and life sciences. |
|
|
Planning and Reporting Continuity: RPP 2007-2008: |
|
|
Resources |
2008-2009 |
2009-2010 |
2010-2011 |
|
Financial ($ in millions) |
115.4 |
93.3 |
79.6 |
|
Human (FTEs) |
188.4 |
181.5 |
179.8 |
The programs under this Program Activity are divided into 3 Sub-Activities: Enabling Research, Space Mission Development and Space Mission Operations.
Enabling Research – Space Science and Exploration
Objective: Provide leadership, coordination or support to Space Science and Exploration (SE) applied research and experimental development in line with the CSA priorities and stakeholders expectations in order to increase the knowledge base and devise new applications through space missions, and to allow the transfer of intellectual property and proven technologies to Canadian industry, academia, and government organizations.
| Expected Result #1 | Performance Indicators |
| New project/mission concepts that progress to subsequent development phases related to Agency priorities. |
|
| Expected Result #2 | Performance Indicators |
| The CSA's in-house personnel are highly qualified, with recognized expertise, and are supported by a high-technology infrastructure that is suited to all enabling research projects/missions. |
|
|
Resources |
2008-2009 |
2009-2010 |
2010-2011 |
|
Financial ($ in millions) |
25.7 |
23.3 |
18.5 |
|
Human (FTEs) |
39.5 |
38.9 |
37.7 |
Main Expected Accomplishments:
- The CSA will continue to participate actively in the International Space Exploration Coordination Group that was created in 2007 to promote coordination of Moon and Mars exploration between various space agencies around the world. The CSA will establish an Exploration Core Program to support the development of prototypes of systems that could become potential contributions to
future Moon or Mars missions. This Program ensures the readiness of the space exploration community in Canada and will be implemented with industry, university and research institutions.
- Maintain a trained and versatile Astronaut Corps to develop and maintain human space flight expertise to meet the requirements of the CSA's space sciences and human exploration programs. Two Canadian astronauts have started training in preparation for an assignment to a long-duration space flight on the ISS in the 2009 timeframe. The CSA will continue to explore activities related to the Advanced Astronaut Medical Support (ADAMS) program. Specifically, CSA will continue to explore solutions to the delivery of health care on future long duration exploration-class missions and how these solutions can help improve healthcare delivery on Earth through the transfer of space technology.
Space Mission Development – Space Science and Exploration
Objective: Provide coordination or support to the development of Space Science and Exploration (SE) space missions in line with CSA priorities and stakeholders expectations through the definition, critical design, manufacturing, integration, testing and delivery phases leading to launch and early operations of space systems.
| Expected Result #1 | Performance Indicator |
| Space mission proposals that efficiently, effectively and economically progress to subsequent operations phases in accordance with objectives, requirements, initial or revised specifications. |
|
| Expected Result #2 | Performance Indicators |
| The CSA's in-house personnel are highly qualified, with recognized expertise, and are supported by a high-technology infrastructure that is suited to all Space mission development projects. |
|
|
Resources |
2008-2009 |
2009-2010 |
2010-2011 |
|
Financial ($ in millions) |
36.0 |
15.6 |
6.5 |
|
Human (FTEs) |
22.1 |
18.1 |
17.1 |
Main Expected Accomplishments:
- The Enhanced Polar Outflow Probe (e-POP) integrated with the CASSIOPE Mission, is scheduled for launch in 2009. The suite of e-POP instruments will undergo environmental testing in the CSA's David Florida Laboratory. The scientific data collected by e-POP will help scientists understand particle exchange and energy coupling processes between the Earth's atmosphere and space
environment.
- The CSAwill deliver to NASA the Alpha Particle X-ray Spectrometer (APXS) for the Mars Science Laboratory to be launched by NASA in 2009. The Canadian contribution will help scientists to determine the chemical composition of various soil, dust and rock samples on the planet.
- Canada is participating in the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) that will be launched in 2013. Canada is responsible for the Fine Guidance Sensor (FGS), which ensures the very precise pointing of the telescope and the provision of simultaneous images. The design of the FGS will be completed and the manufacturing will continue in 2008-2009. By virtue of the CSA's contribution,
Canadian astronomers will have guaranteed access to 5% of the observing time of the James Webb Space Telescope.
- The Local Oscillator Source Unit (LSU) that was successfully integrated in the Heterodyne Instrument for the Far Infrared (HIFI) of the European Space Agency's Herschel satellite will be launched in 2008. The satellite will carry an infrared telescope and three scientific instruments that will allow scientists to address key science questions such as how galaxies were formed in the early universe and how stars have been forming throughout the history of the universe.
Space Mission Operations – Space Science and Exploration
Objective: Provide coordination or support to the operations of Space Science and Exploration (SE) space missions in line with the CSA priorities and stakeholders' expectations through the development and conduct of on-orbit operations, system maintenance and logistic support, as well as data handling and delivery.
| Expected Result #1 | Performance Indicator |
| Space mission operations are managed effectively and efficiently. |
|
| Expected Result #2 | Performance Indicators |
| The CSA's in-house personnel are highly qualified, with recognized expertise, and are supported by a high-technology infrastructure that is suited to all Space mission operations. |
|
|
Resources |
2008-2009 |
2009-2010 |
2010-2011 |
|
Financial ($ in millions) |
53.8 |
54.4 |
54.6 |
|
Human (FTEs) |
126.8 |
124.5 |
124.9 |
Main Expected Accomplishments:
- On the International Space Station, CSA will upgrade its ground control operations of Canadarm2 enabling the handling of heavy payloads from the ground, and will initiate limited ground control operations of Dextre (Special Purpose Dexterous Manipulator) to be launched in March 2008 on Shuttle mission STS-123/1J/A. The development of expanded ground control capabilities will
reduce significantly astronaut time requirement for future Dextre operations.
- The Phoenix mission, successfully launched in August 2007, is targeted to land on the northern polar region of Mars on May 25th, 2008. It will provide basic scientific knowledge of the Martian atmosphere, and will permit Canadian scientists to have access to all data from the mission. This mission will position Canada as a respected and reliable provider of planetary science
instrumentation.
- The CSA will continue the analysis of the e-OSTEO space mission scientific experiments that were successfully completed in September 2007. These experiments focus on bone loss in space that is one of the major obstacles to long duration spaceflight.
To learn more about Space Science and Exploration Program Activity, go to: www.space.gc.ca/asc/eng/resources/publications/default.asp#parliament
To learn more about Space Science and Exploration, go to: www.space.gc.ca/asc/eng/sciences/default.asp and, www.space.gc.ca/asc/eng/exploration/default.asp
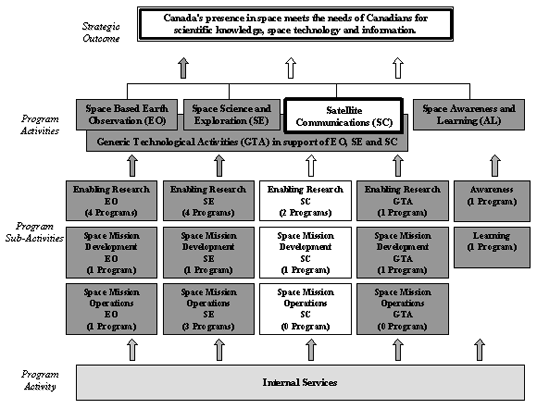
2.3 Satellite Communications
Program Activity Priority: Provide all Canadians with the means to participate in and fully benefit from the global information age.
|
Satellite Communications (SC) Program Activity Performance Measurement |
|
|---|---|
| Expected Result #1 | Performance Indicators |
|
The systems and applications developed satisfy the needs of Canadians and of the Canadian government that are not being met by existing commercial systems and applications. |
|
|
Planning and Reporting Continuity: RPP 2007-2008: |
|
|
Resources |
2008-2009 |
2009-2010 |
2010-2011 |
|
Financial ($ in millions) |
26.7 |
18.7 |
14.5 |
|
Human (FTEs) |
12.9 |
14.0 |
14.2 |
The programs under this Program Activity are divided into three Sub-Activities: Enabling Research, Space Mission Development and Space Mission Operations. However, no Space Mission Operations are mentioned in this report.
Enabling Research – Satellite Communications
Objective: Provide leadership, coordination or support to Satellite Communications (SC) applied research and experimental development in line with the CSA priorities and stakeholders expectations in order to increase the knowledge base and devise new applications through space missions, and to allow the transfer of intellectual property and proven technologies to Canadian industry, academia, and government organizations.
| Expected Result #1 | Performance Indicators |
| New project/mission concepts that progress to subsequent development phases related to Agency priorities. |
|
| Expected Result #2 | Performance Indicators |
| The CSA's in-house personnel are highly qualified, with recognized expertise, and are supported by a high-technology infrastructure that is suited to all enabling research projects/missions. |
|
|
Resources |
2008-2009 |
2009-2010 |
2010-2011 |
|
Financial ($ in millions) |
16.6 |
15.3 |
13.5 |
|
Human (FTEs) |
6.0 |
6.0 |
6.0 |
Main Expected Accomplishments:
- The CSA will continue to work towards the utilization of the Anik F2 Government of Canada capacity credit for broadband telecommunications services in the North. Additional demonstration of Ka-band technology will improve the use of the Anik F2 satellite by northern communities for trials of innovative Canadian government services and in specific areas of interest to other
government departments.
- The CSA will complete the assessment of the telecommunications requirements of federal government users in order to support the definition of two mission concepts in 2008-2009. They are:
- The next Generation Satellite Communication Payload Mission, consisting of an advanced V-Band transporter on board on Telesat's future Anik satellites.
- The Polar Communications and Weather Satellite, consisting of a high data rate communications providing coverage of the polar cap in the high Arctic.
- The next Generation Satellite Communication Payload Mission, consisting of an advanced V-Band transporter on board on Telesat's future Anik satellites.
Space Mission Development – Satellite Communications
Objective: Provide coordination or support to the development of Satellite Communications (SC) space missions in line with CSA priorities and stakeholders expectations through the definition, critical design, manufacturing, integration, testing and delivery phases leading to launch and early operations of space systems.
| Expected Result #1 | Performance Indicator |
| Space mission proposals that efficiently, effectively and economically progress to subsequent operations phases in accordance with objectives, requirements, initial or revised specifications. |
|
| Expected Result #2 | Performance Indicators |
| The CSA's in-house personnel are highly qualified, with recognized expertise, and are supported by a high-technology infrastructure that is suited to all Space mission development projects. |
|
|
Resources |
2008-2009 |
2009-2010 |
2010-2011 |
|
Financial ($ in millions) |
10.1 |
3.4 |
1.0 |
|
Human (FTEs) |
6.9 |
8.0 |
8.2 |
Main Expected Accomplishments:
In 2004-2005, as part of the CASSIOPE Mission Contribution Program, the CSA initiated the development and demonstration of the Cascade telecommunications payload on a small satellite bus. This small satellite spacecraft is being designed and constructed by Canadian companies. During 2008, integration and environmental testing of the spacecraft will be completed and the launch is planned in 2009. Cascade is the precursor of a communication satellite constellation that will help position Canadian industry on the international market, both as a supplier of advanced components and as a service provider of high-volume, high-data-rate telecommunications anywhere in the world.
To learn more about Satellite Communications Program Activity, go to: www.space.gc.ca/asc/eng/resources/publications/default.asp#parliament
To learn more about Satellite Communications, go to: www.space.gc.ca/asc/eng/satellites/default.asp
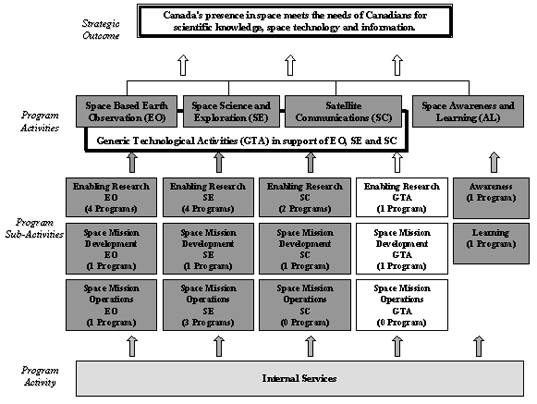
2.4 Generic Technological Activities in support of Earth Observation, Space Science and Exploration, and Satellite Communications
Program Activity Priority: Provide leadership, co-ordination or support to Earth Observation (EO), Space Science and Exploration (SE), and Satellite Communications (SC) Program Activities through activities that are generic.
|
Generic Technological Activities (GTA) in Support of EO, SE, and SC Program Activity Performance Measurement |
|
|---|---|
| Expected Result #1 | Performance Indicators |
|
Canada's industrial technological capabilities can meet the needs of future space missions and activities. |
|
|
Planning and Reporting Continuity: RPP 2007-2008: |
|
|
Resources |
2008-2009 |
2009-2010 |
2010-2011 |
|
Financial ($ in millions) |
48.3 |
61.4 |
60.9 |
|
Human (FTEs) |
141.4 |
146.6 |
161.6 |
The programs under this Program Activity are divided into three Sub-Activities: Enabling Research, Space Mission Development and Space Mission Operations. However, no Space Mission Operations are mentioned in this report.
Enabling Research – Generic Technological Activities in Support of EO, SE, and SC
Objective: Provide leadership, coordination or support EO, SE and SC applied research and experimental development in line with the CSA priorities and stakeholders expectations.
| Expected Result #1 | Performance Indicator |
| Space technology concepts that support projects/missions related to Agency priorities. |
|
| Expected Result #2 | Performance Indicators |
| Canadian industries and research organizations that are actively involved in space research and development. |
|
|
Resources |
2008-2009 |
2009-2010 |
2010-2011 |
|
Financial ($ in millions) |
40.5 |
52.5 |
52.6 |
|
Human (FTEs) |
96.9 |
102.1 |
116.6 |
Main Expected Accomplishments:
- The Space Technology Development Program (STDP) addresses priority technologies required for national and international space missions and activities of interest to the CSA programs. Through periodic Requests for Proposal, STDP awards R&D contracts to industry and research organizations to create mission concepts, propose innovative technologies, retire risk on the
critical technologies required for future missions, and contribute to the enhancement of Canadian capabilities through the demonstration of new products and services.
- Through the Space Technology Research Program develop long-term high-risk space technologies and maintain in-house technical capabilities by conducting advanced R&D projects that meet the criteria of excellence and relevance in support of the implementation of the CSA space programs.
Space Mission Development – Generic Technological Activities in Support of EO, SE, and SC
Objective: Provide coordination or support to the development of EO, SE and SC space missions in line with CSA priorities and stakeholders expectations through the definition, critical design, manufacturing, integration, testing and delivery phases leading to launch and early operations of space systems.
| Expected Result #1 | Performance Indicators |
| The CSA's in-house personnel are highly qualified, with recognized expertise, and are supported by a high-technology infrastructure that is suited to all Space mission development projects. |
|
|
Resources |
2008-2009 |
2009-2010 |
2010-2011 |
|
Financial ($ in millions) |
7.8 |
8.9 |
8.3 |
|
Human (FTEs) |
44.5 |
44.5 |
45.0 |
Main Expected Accomplishments:
David Florida Laboratory provides world-class and cost-effective environmental space qualification services for the assembly, integration and testing of spacecraft systems and sub-systems to all of the CSA's programs. Many projects will benefit from DFL support, such as for:
- Science and Exploration: CASSIOPE e-POP mission; Neossat; James Webb Space Telescope (JWST); and the UltraViolet Imaging Telescope (UVIT);
- Satellite Communications: CASSIOPE Cascade mission;
- Commercial Programs: Various spacecraft from Space Systems Loral, MDA (SSRMS & SRMS), TenXc Wireless (PCS Antennas), Inmarsat Aeronautical Antennas, Harris Corporation (MUOS); and,
- Other Government Departments: DND CF-18 Radome Characterization Project.
To learn more about Generic Technological Activities Program Activity, go to: www.space.gc.ca/asc/eng/resources/publications/default.asp#parliament
To learn more about Generic Technological Activities Supporting Earth Observation, Space Science and Exploration, and Satellite Communications, go to: www.space.gc.ca/asc/eng/industry/technology.asp
To learn more about the David Florida Laboratory, go to: www.space.gc.ca/asc/eng/dfl/default.asp
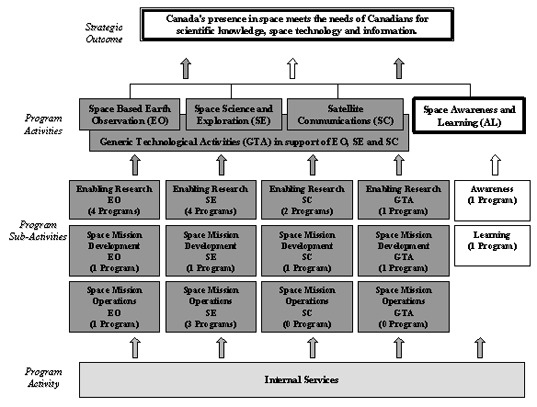
2.5 Space Awareness and Learning
Program Activity Priority: Further public understanding and engagement with regards to space-related issues, ultimately leading to improving the scientific literacy of Canadians.
|
Space Awareness and Learning Program Activity Performance Measurement |
|
|---|---|
| Expected Result #1 | Performance Indicator |
|
Targeted level of awareness of Canadians towards space is reached. |
|
|
Planning and Reporting Continuity: RPP 2007-2008: |
|
|
Resources |
2008-2009 |
2009-2010 |
2010-2011 |
|
Financial ($ in millions) |
7.9 |
8.9 |
8.8 |
|
Human (FTEs) |
29.0 |
29.0 |
29.0 |
This Program Activity is divided into two Sub-Activities: Awareness and Learning.
Awareness
Objective: Increase public awareness and understanding of how space affects and improves the quality of life.
| Expected Result #1 | Performance Indicator |
|
Target audience is reached through outreach activities. |
|
|
Resources |
2008-2009 |
2009-2010 |
2010-2011 |
|
Financial ($ in millions) |
5.1 |
5.9 |
5.9 |
|
Human (FTEs) |
24.0 |
24.0 |
24.0 |
Main Expected Accomplishments:
The major communications activities will focus on the following:
- Awareness campaign related to the launch of Dextre, the final component and contribution of Canada's advanced space robotics suite to the ISS, a two-armed dexterous manipulator that will enhance construction and maintenance of the International Space Station.
- Celebration of the 10th anniversary of the International Space Station; continuing promotion of Canada's key role as a member and contribution of critical scientific and technological expertise, and suite of space robotics that is building and maintaining the Space Station.
- Promotion of the successful commissioning of Canada's most advanced Earth Observation imaging satellite, RADARSAT-2. As RADARSAT-2 is fully tested and declared operational, it will begin production of precise imaging for Government and commercial clients.
- Awareness campaign related to Mars landing of NASA's Phoenix Mars Rover with a Canadian science instrument and weather station aboard.
Learning
Objective: Direct a sustained multi-dimensional and inter-active learning program to build knowledge and enhance interest in space science and technology.
| Expected Result #1 | Performance Indicators |
|
Canadian educators and students further their learning related to science and technology through space theme. |
|
|
Resources |
2008-2009 |
2009-2010 |
2010-2011 |
|
Financial ($ in millions) |
2.8 |
3.0 |
3.0 |
|
Human (FTEs) |
5.0 |
5.0 |
5.0 |
Main Expected Accomplishments:
- Professional development workshops and teaching initiatives such as satellite enabled or web-based assisted tele-learning opportunities for educators.
- Partnered initiatives with schools, youth organisations and other institutions to expand student and educator access to the space science and technology community and space-learning materials.
- Targeted grants, contribution and sponsorship programs in partnership with other federal departments and agencies to support awareness, research, development and training in space science and technology.
To learn more about Space Awareness and Learning Program Activity, go to: www.space.gc.ca/asc/eng/resources/publications/default.asp - parliament
To learn more about Space Awareness and Learning, go to: www.space.gc.ca/asc/eng/media/default.asp; and, www.space.gc.ca/asc/eng/educators/default.asp
2.6 Internal Services
Program Activity Priority: To implement the government's commitment to modern public service management in accordance with the Management Accountability Frameworks (MAF) expectations.
|
Internal Services Program Activity Performance Measurement |
|
| Expected Result #1 | Performance Indicator |
|
Internal Services provide an added value to CSA managers in the performance of their duties. |
Services provided meet standards set under Government-wide and CSA policies as well as MAF expectations. |
| Expected Result #2 | Performance Indicators |
|---|---|
|
The four highest priority risks identified in the CSA corporate risk profile are addressed and mitigated:
1. Values and Ethics: Increase the capacity of the CSA to instill public service values, to develop a working environment free of harassment, and promoting respect for individuals, integrity and honesty. 2. Workforce Competencies: Increase the capacity of CSA to maintain a qualified workforce of public servants to deliver CSA's mandate within the government legislative frameworks, policies and rules.
|
Management and mitigation actions are implemented:
2.2. The majority of CSA managers are recognized as being qualified for increased delegation of authority. (Target: Full hiring delegated authority is granted by the Public Service Commission by September 2008.) 3.1. The corporate Work Planning information system (eWP) is fully implemented and functional for all sectors for the planning of 2008-2009 and monitoring of 2007-2008. 3.2. Completed development of a Long-term Investment Plan. (Target: The Plan is approved by CSA Executive Committee) |
|
Planning and Reporting Continuity: RPP 2007-2008: |
|
|
Resources |
2008-2009 |
2009-2010 |
2010-2011 |
|
Financial ($ in millions) |
40.6 |
39.9 |
39.9 |
|
Human (FTEs) |
270.1 |
269.3 |
270.1 |
Main Expected Accomplishments:
The Internal Services Program Activity covers the following sub-activities: Management and Oversight, Human Resources Management, Financial Management, Supply Chain Management, Facilities and Asset Management, Information Management, Information Technology, Public Affairs and Communications, Program Evaluation, Internal Audit, and Legal Services. As part of their current activities, Internal Services will carry out key activities and service provision improvements such as:
Management and Oversight
- Finalize the measurement strategy for the full deployment of the Performance Measurement Framework (PMF).
- Ensure that corporate priority review exercise is completed in time for the 2009-2010 ARLU exercise.
Evaluation and Internal Audit Services
- The following evaluations will be completed in 2008-2009:
- RADARSAT-1 and RADARSAT-2 Major Crown Projects;
- CASSIOPE Mission Grants & Contributions Program; and,
- Canada/ESA Cooperation Agreement.
- Create an independent Departmental Audit Committee made of a majority of members from outside the federal public service.
- Develop of a risk-based multi-year internal audit plan.
Finance Services
- Implement internal control procedures in order to assure managers that all payments are compliant with current financial policies.
- Develop a forecast module in the expenditure management system in order to optimize the spending of allocated funds.
Human Resources
- The Integrated Corporate Human Resources Plan developed in 2007-2008 will be implemented by all CSA sectors.
- Establish the profile of essential competencies by which full delegation authority will be granted to managers and make sure that a majority of managers are qualified.